Grounding Carbon Brush RS93/EH7Us
Product Description
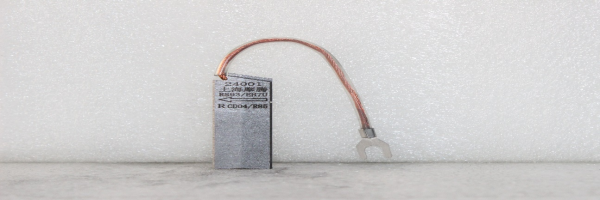
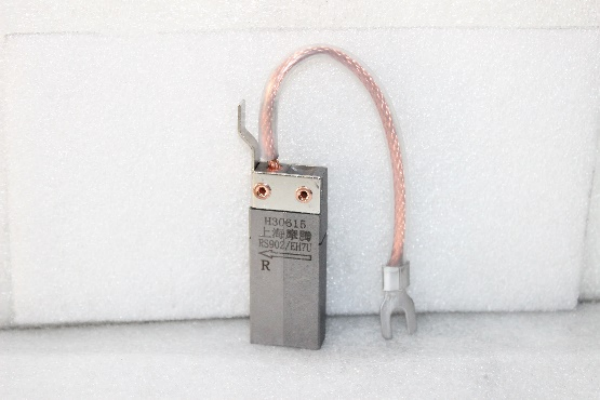
|
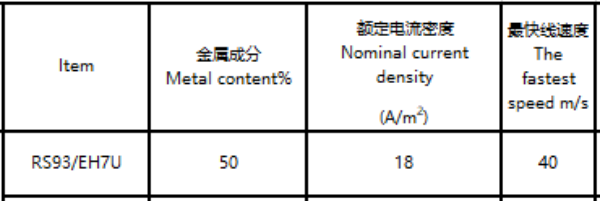
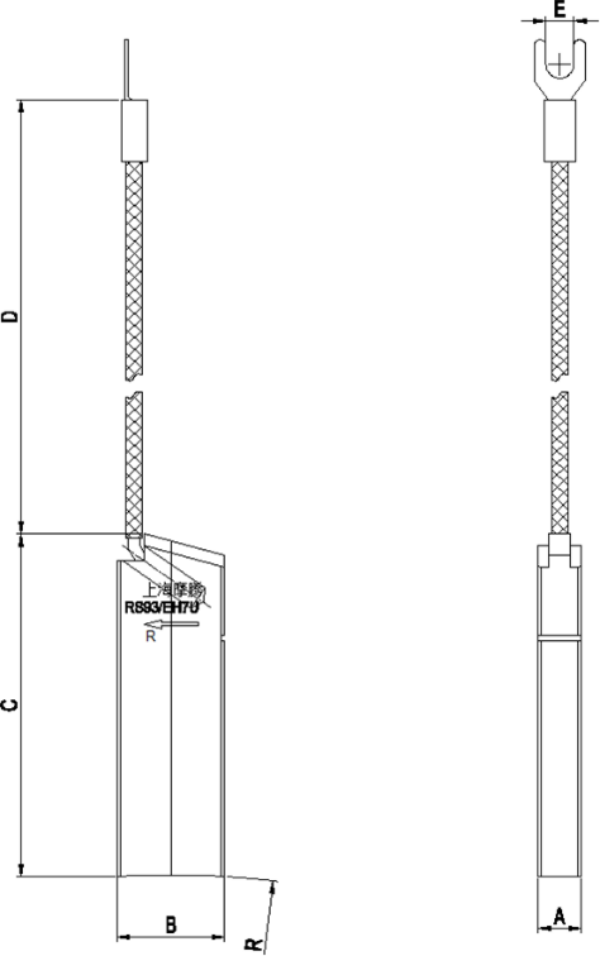
Basic dimensions and characteristics of carbon brush |
|||||||
|
Drawing No. |
牌号 |
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
R |
| MDFD-R080200-125-09 |
RS93/EH7U |
8 |
20 |
50 |
100 |
6.5 |
R140 |
| MDFD-R080200-126-09 |
RS93/EH7U |
8 |
20 |
50 |
100 |
6.5 |
R140 |
| MDFD-R080200-127-10 |
RS93/EH7U |
8 |
20 |
64 |
110 |
6.5 |
R85 |
| MDFD-R080200-128-10 |
RS93/EH7U |
8 |
20 |
64 |
110 |
6.5 |
R85 |
| MDFD-R080200-129-04 |
RS93/EH7U |
8 |
20 |
32 |
75 |
6.5 |
R125 |
| MDFD-R080200-130-04 |
RS93/EH7U |
8 |
20 |
32 |
75 |
6.5 |
R125 |
| MDFD-R080200-131-01 |
RS93/EH7U |
8 |
20 |
32 |
75 |
6.5 |
R160 |
| MDFD-R080200-132-01 |
RS93/EH7U |
8 |
20 |
32 |
75 |
6.5 |
R160 |
Technical Specification Parameters
The role of grounded carbon brushes in electrical systems is essential across various applications. Carbon brushes are vital for ensuring the smooth performance of motors and the efficient transfer of current, serving as key components in both brushed and brushless DC motors, as well as specific types of AC motors.
In brushed DC motors, carbon brushes have several important functions. Primarily, they supply external or excitation current to the rotating rotor, acting as a conductive pathway, which is crucial for the motor's functionality. Additionally, the carbon brush introduces a static charge on the rotor shaft, effectively grounding it. This grounded carbon brush facilitates the output current, promoting a consistent flow of electricity within the system. It also assists in altering the direction of the current, and in commutator motors, it supports the commutation process. Furthermore, the brush connects the rotor shaft to a protection device for grounding purposes and enables the measurement of positive and negative voltages relative to ground.
The commutator, composed of brushes and commutation rings, is a vital component in brushed DC motors. Due to the rotor's rotation, the brush consistently experiences friction against the commutation ring, which can lead to spark erosion during the commutation process. This wear and tear classify the carbon brush as a consumable part in DC motors. To mitigate these challenges, brushless DC motors have been developed as a more durable alternative, aiming to enhance service life, operational stability, and minimize noise and electromagnetic interference.
It is noteworthy that AC motors typically do not utilize brushes or a commutator, as they function without a constant magnetic field. However, AC motors are generally larger than their DC counterparts. This difference highlights the significance of carbon brushes in the operation of DC motors and illustrates the ongoing advancements in motor technology.
In summary, the function of grounded carbon brushes is integral to the efficient operation of various motor types. As technology evolves, the importance of carbon brushes in electrical systems remains a critical factor in ensuring motor performance and reliability.













